|
PYtest (14C-Urea Capsules)DescriptionPYtest (14C-urea capsules) is intended for use in the detection of gastric urease as an aid in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori (H.pylori) infection in the human stomach. The test utilizes a liquid scintillation counter for the measurement of 14CO2 in breath samples. The capsules are to be used when analysis is planned at the site where the sample is taken. PYtest capsule is a gelatin capsule for oral administration containing 1uCi of 14C labeled urea. The urea is adsorbed on sugar spheres and colored yellow with fluorescein. Data on 14C-urea:Structural Formula: (14C-urea): NH2 14CONH2 Radiation emission: beta-emission, 49 keVmean, 156 keVmax, no other emissions External emission: No external radiation hazard. Low-energy beta emissions only. Maximum range of 0.3 mm in water. Radiological Half-life: 5730 years Maximum effective dose equivalent (EDE) : 0.3 mrem/µCi Clinical Pharmacology |
|
The urease enzyme is not present in mammalian cells, so the presence of urease in the stomach is evidence that bacteria are present. The presence of urease is not specific for H.pylori, but other bacteria are not usually found in the stomach. The principle of the breath test is shown in Figure 1. To detect H.pylori, urea labeled with 14C is swallowed by the patient. If gastric urease from H.pylori is present, urea is split to form CO2 and NH3 at the interface between the gastric epithelium and lumen, and the 14CO2 is absorbed into the blood and exhaled in the breath. |
 |
|
Following ingestion of the capsule by a patient with H.pylori, 14CO2 excretion in the breath peaks between 10 and 15 minutes and declines thereafter with a biological half-life of about 15 minutes. 14C-urea that is not hydrolyzed by H.pylori is excreted in the urine with a half-life of approximately 12 hours. About 10% of the 14C remains in the body at 72 hours and is gradually excreted with a biological half-life of 40 days. Clinical StudiesTwo studies were performed. In both studies, patients with gastrointestinal symptoms underwent the breath test and an endoscopy. During the endoscopy, biopsy samples were taken from antral gastric mucosa for histological analysis (2 samples, Giemsa stain) and rapid urease test (1 sample, CLOtestÒ ). Breath samples were mailed to the TRI-MED lab where they were read in a liquid scintillation counter. Results were reported as disintegrations per minute (DPM). Analysis for accuracy used the ten minute breath sample. A breath sample DPM <50 was defined as a negative result. DPM ³ 200 was defined as a positive result. DPM in the range of 50-199 was classified as indeterminate. Study 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Histology and CLOtest | ||||||
|
H.pylori |
Positive |
Negative |
Total |
|||
|
PYtest |
Positive |
51 |
8 |
59 |
ppv. |
86% |
|
(DPM 10m) |
Indeterminate |
1 |
8 |
9 |
||
|
|
Negative |
1 |
117 |
118 |
npv. |
99% |
|
Total |
53 |
133 |
186 |
|||
|
sensitivity |
specificity |
|||||
|
96% |
88% |
|||||
Notes: PYtest at 10 min. was compared to the gold standard of biopsy results in which histology and CLOtest concurred. Patients who did not have both biopsy tests performed, or in whom the tests differed, were excluded from analysis. There was no statistical difference in test accuracy based on gender of patient.
ppv = positive predictive value
(total PYtest positive divided by true positive)
npv = negative predictive value (total PYtest
negative divided by true negative)
Study 2
Breath tests were performed on
436 outpatients attending gastroenterology practices at sites in the
United States. Seventy-six patients (40 men,36 women) who
had histology and CLOtest were evaluated. The results are summarized
below:
Study #2 (n=76, Indeterminate results included)
|
Histology and CLOtest | ||||||
|
H.pylori |
Positive |
Negative |
Total |
|||
|
PYtest |
Positive |
22 |
0 |
22 |
ppv. |
100% |
|
(DPM 10m) |
Indeterminate |
4 |
2 |
6 |
||
|
|
Negative |
1 |
47 |
48 |
npv. |
98% |
|
Total |
27 |
49 |
76 |
|||
|
sensitivity |
specificity |
|||||
|
82% |
96% |
|||||
Notes: PYtest at 10 min. was compared to the gold standard of biopsy results in which histology and CLOtest concurred. Patients who did not have both biopsy tests performed, or in whom the tests differed, were excluded from analysis. There was no statistical difference in test accuracy based on gender of patient.
ppv = positive predictive value
(total PYtest positive divided by true
positive)
npv =
negative predictive value (total PYtest negative divided by true negative)
Indications and Usage
PYtest (14C-urea breath test) is indicated for use in the detection of gastric urease as an aid in the diagnosis of H.pylori infection in the human stomach. The test utilizes a liquid scintillation counter for the measurement of 14CO2 in breath samples.
Contraindications
None
Warnings
None
Precautions
General:After the patient ingests the 14C urea capsule, the sample collected for test purposes is for in vitro diagnostic use only.
A false positive test could occur in patients who have achlorhydria. Very rarely, a false positive test may occur due to urease associated with Helicobacters other than H.pylori (i.e. Helicobacter heilmanni).
Limitations of the Test:- The test has been evaluated in outpatients attending for elective endoscopy.
- Test results should be evaluated with clinical signs and patient history when diagnosing H. pylori infection.
- The performance characteristics of the test have not been established for monitoring the efficacy of antimicrobial therapies for the treatment of H.pylori infection.
- A negative result does not completely rule out the possibility of H. pylori infection. If clinical signs and patient history suggest H. pylori infection, repeat the PYtest or use an alternative diagnostic method.
Persons concerned about very low doses of radioactivity may postpone the test or may decide to use an alternative means of diagnosis. The test produces radiation exposure equal to 24 hours of normal background. In animal experiments, such low doses of radiation do not carry measurable risk.
Preclinical studies were not conducted on 14C-urea. The estimated dose equivalent received from a single administration of PYtest (1m 14C -urea) is about 0.3 mrem. An individual radiation dose of 5-10 mrem is below regulatory concern as recommended by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
Information for Patients:It is necessary for the patient to fast for 6 hours before the test. The patient should also be off antibiotics and bismuth for 1 month, and proton pump inhibitors and sucralfate for 2 weeks prior to the test. Instruct the patient not to handle the capsule directly as this may interfere with the test result. The capsule should be swallowed intact. Do not chew the capsule.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility:No studies have been conducted with 14C- urea to evaluate its potential for carcinogenicity, impairment of fertility, or mutagenicity.
Drug Interactions:Antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, sucralfate, and bismuth preparations are known to suppress H.pylori. Ingestion of antibiotics or bismuth within 4 weeks and proton pump inhibitors or sucralfate within 2 weeks prior to performing the test may give false negative results.
Pregnancy:Pregnancy category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with PYtest ( 14C- urea). It is also not known whether PYtest can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. PYtest should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers:It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when PYtest is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric use:Clinical studies in children have not been conducted. However, PYtest is expected to work the same in children as in adults. While the dose (1 capsule) does not need to be adjusted, the child must be able to swallow the intact capsule and blow into a straw.
Adverse Reactions
No adverse reactions were reported in clinical trials.
Overdosage
Risk from radiation is negligible even with a 1000 capsule overdose (0.3 rem). If overdose occurs the patient may drink one glass of water (150 mL) every hour to hasten excretion of the isotope. Maximum excretion of urea is achieved at a urine output of ³ 2.0 mL/min.
Dosage and Administration
Materials Needed but not Provided
For analysis at test site
Breath Sample Collected into Balloon (recommended method)
- Breath test report form
- Stopwatch/Timer capable of timing an interval up to 10 minutes.
- Marking pen
- 1-20mL scintillation vial
- Breath transfer pump*
- Pipette (10 mL) for measuring fluids
- Collection fluid (2.5cc per vial)
- Scintillation fluid (10 cc/vial)
- 1- Mylar collection balloon
- 1 - Straw
- 2 - Needles
- 2 - 30 ml medicine cups
- Water (40mL)
*Any gas pump that is airtight and has a flow rate between .5 and 1 liter per minute may be used.
For analysis at test site:
Breath Sample Collected into Vial
CAUTION - TRI-MED Specialties, Inc. does not endorse breath sample collection by this method because patients might come into direct contact with the hyamine.
- Breath test report form
- Stopwatch/Timer capable of timing an interval up to 10 minutes
- Safety trap (Figure 3)
- 1 - Straw
- 1 - 20mL scintillation vial
- Marking pen
- Pipette (10mL) for measuring fluids
- Collection fluid (2.5 cc/vial)
- Scintillation fluid (10 cc/vial)
Typical Safety Trap
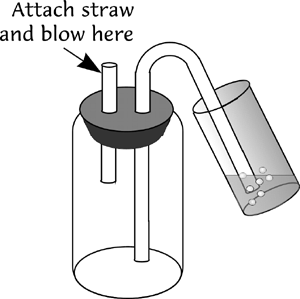
Dosage
One PYtest capsule.
Procedural Notes
- Inform the patient to fast for 6 hours prior to the test.
- The patient should also be off antibiotics and bismuth for 1 month, and proton pump inhibitors and sucralfate for 2 weeks prior to the test.
- Have patient sitting at rest while doing the test.
- The capsule should not be handled directly as this may interfere with the test result.
- To avoid contamination by bacteria in the mouth, the capsule should be swallowed intact. Do not chew capsule.
Step by Step Procedure for Balloon:
Breath Sample Collection by Balloon
|
Before the test |
1. Label balloon and fill in breath test report form. 2. Check that all materials are present. |
|
Minus 1 minute |
1. Open the package containing the 14C-urea capsule and tip the capsule into the empty 30 mL cup. Do not handle the capsule directly. 2. Hand the cup to the patient. 3. Fill the second cup with 20 mL lukewarm water. |
|
0 minute |
1. Ask the patient to tip the capsule directly into his/her mouth, then swallow it with the 20 mL of lukewarm water. 2. Start the stopwatch when the patient swallows the capsule. 3. Discard waste (e.g. capsule packaging, used straw) according to your facility’s regulations. |
|
3 minutes |
Ask the patient to drink another 20 mL of lukewarm water (in case the capsule may have lodged in the esophagus and not yet reached the gastric mucosa). |
|
10 minutes |
1. Push a drinking straw into the neck of the balloon. 2. Ask the patient to hold his/her breath for 5-10 seconds, then blow up the balloon with a slow breath through the straw, filling the balloon completely. 3. Tie the neck of the balloon into a tight knot. 4. Check that the balloon label and the breath test report form are completed correctly. |
|
After sample collection |
See test analysis procedure |
Breath Sample Collection by Vial:
CAUTION- Tri-Med Specialties, Inc. does not endorse the collection of breath samples by this method for patient safety reasons.
|
Before the test |
1. Label vial and fill in breath test report form. Vial label should include the patient’s name, date of sample collection and time sample is taken. 2. Check that the vial contains 2.5 mL of collection fluid (1.5 mL methanol, 1.0 mL 1 molar hyamine, two drops thymolphthalein pH indicator). 3. Check that all materials are present. |
|
Minus 2 minutes |
Attach a straw to the safety trap (Figure 3). |
|
Minus 1 minute |
1. Open the package containing the 14C -urea capsule and tip the capsule into the 30 mL cup. Do not handle the capsule directly. 2. Hand the cup to the patient. 3. Fill the second cup with 20 mL lukewarm water. |
|
0 minute |
1. Ask the patient to tip the capsule directly into his/her mouth, then swallow it with the 20 mL of lukewarm water. 2. Start the stopwatch when the patient swallows the capsule. 3. Discard waste (e.g., capsule packaging, used straw) according to your facility’s regulations. |
|
3 minutes |
Ask the patient to drink another 20 mL of lukewarm water (in case the capsule may have lodged in the esophagus and not yet reached the gastric mucosa). |
|
10 minutes |
Ask the patient to hold his/her breath for 5-10 seconds, then blow bubbles into the collection fluid via the safety trap. The patient should blow bubbles until the fluid turns clear. Put lid on vial. |
|
After sample collection |
See test analysis procedure. |
Test Analysis Procedure
General Information
- The collection fluid contains hyamine, methanol and a pH indicator. Hyamine is a corrosive caustic alkali. If you are using the vial method and collecting breath directly into the collection fluid you must supervise the patient and ensure that a safety trap is used.
- The amount of hyamine (1 mL of 1 molar) and methanol (2.5 mL) in one collection vial is not sufficient to cause serious poisoning. Local irritation to skin or mucous membranes is likely when the solution is blue. After collecting CO2 the collection fluid turns clear. At this point it is less dangerous because the pH is near neutral.
- If the collection fluid splashes onto the skin or eyes, wash immediately with water. If the collection fluid is accidentally ingested, wash the mouth with water and have the patient drink 250mL of water immediately. Consult your poison information center for further facts on hyamine.
- Scintillation fluid comes in many formulations. It is usually a mixture of toluene and various cyclic hydrocarbons. It is flammable. Biodegradable formulations do exist. Consult your supplier if you have questions
Balloon Read on Site:
- Add 2.5cc collection fluid to each vial.
- Label the scintillation vial lid to match the label on the balloon.
- Attach a needle to the inlet and outlet tubes on the pump.
- Turn on pump. Allow to run for about 15 seconds.
- Put needle from the rigid outlet tube in a vial until it makes bubbles in the collection fluid.
- Pierce the label of a filled balloon with the other needle and hold it in a stable position. (Do not pierce the balloon anywhere else or it may tear. Do not squeeze the balloon.)
- After 2-3 minutes the collection fluid should turn colorless.
- After the collection fluid is colorless, remove the needles from the balloon and collection fluid and discard according to your facility protocol.
- Change needles between patients.
- Turn off pump after last patient sample is transferred.
- Double check that the label on the vial lid matches the label on the balloon.
- Add 10 mLs scintillation fluid to each vial and mix fluid.
- Count the sample in liquid scintillation counter for 5 minutes or as directed by the liquid scintillation counter manufacturer. (Note that values of 50-300 CPM can occur immediately after the addition of the scintillation fluid due to chemiluminescence. Chemiluminescence decays rapidly over an hour or two and will reveal itself by falling counts. Read the sample repeatedly until values 10 minutes apart are similar. If DPM is still 50-300, you should allow the sample to settle for 12-24 hours before re-testing).
- Include a standard and a blank control vial in each run.
Vial Read on Site:
See steps 12-14 under "Balloon read on-site".
Quality Control:
A minimum of 1 mmol of CO2 is required to perform analysis of a breath sample. The amount of breath required to provide 1 mmol of CO2 varies depending on the amount of CO2 the patient is producing. Since a full balloon typically contains at least 1 mmol of CO2, the balloon should be completely filled.
Results
Interpretation of results (10 minute sample)
|
<50 DPM |
Negative for H.pylori |
|
50-199 DPM |
Indeterminate for H.pylori |
|
³ 200 DPM |
Positive for H.pylori |
DPM = Disintegrations per minute
The indeterminate result should be evaluated by repeating the PYtest or using an alternative diagnostic method. If repeat breath testing is undertaken, careful history to exclude confounding factors should be obtained. If confounding factors are identified, wait an appropriate time (refer to table 3) before repeating the PYtest.
The cutoff point of 50 DPM was determined to be the mean +3SD of results obtained in patients who did not have H.pylori.
Factors which might cause sub-optimal breath test results
|
Factor |
Result |
Comment |
|
Recent antibiotic or bismuth (Pepto-Bismol, etc.) |
false neg. |
Relapse of partially treated HP may take 1-4 weeks. |
|
Omeprazole (or other proton pump inhibitors) |
false neg. |
These agents suppress HP in 40% of patients. Discontinue for at least 2 weeks before performing the PYtest. |
|
Resective gastric surgery |
false neg. |
Isotope may empty rapidly from the stomach. |
|
Resective gastric surgery |
false pos. |
Patient may be achlorhydric and have bacterial overgrowth (non-HP urease). |
|
Food in stomach (also bezoar, gastroparesis) |
unknown |
Isotope may not come into contact with gastric mucosa. Patient may be achlorhydric and/or have bacterial overgrowth (non-HP urease). |
Expected Values
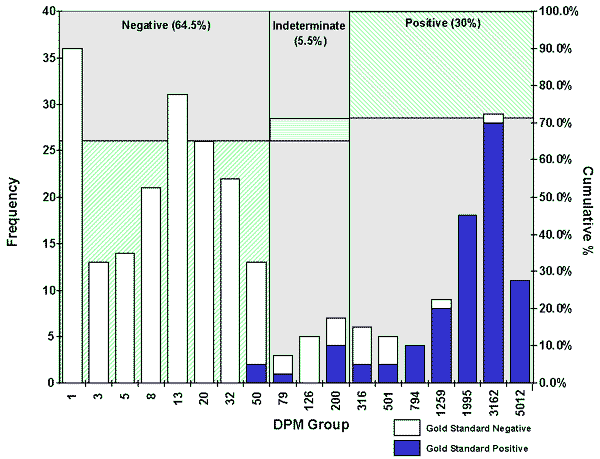
As shown below approximately 30% of patients tested will be positive for H.pylori.
Histogram showing DPM distribution for the PYtest.
*Note: DPM groupings were calculated on a logarithmic
scale. Empty DPM groupings were not included. Chart includes all patients
from Studies 1 and 2. Frequency of DPM group includes samples with DPM
< Group Name.
DPM =
Disintegrations per minute
Gold
Standard = Agreement between histology and CLOtest
If the capsule is damaged or appears abnormal in any way, it may give inaccurate results.
How Supplied
PYtest Capsules, clear gelatin capsules each containing 1uCi of 14C-urea in unit dose packages of 1, 10 and 100.
PYtest Kit (14C-urea breath test) is also supplied as a kit containing a PYtest Capsule and breath collection equipment.
The PYtest Capsule has a shelf life of two years. The expiration date is printed on the capsule label.
PYtest Capsules and Kit should be stored at 15° - 30° C (59° - 86° F) in an area designated by each individual institution’s regulations.
Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law prohibits dispensing without prescription.
Please call TRI-MED Specialties, Inc. at 1-800-874-6331 with any questions , or visit our web site at www.trimed.com.
|
Manufactured by: |
TRI-MED Specialties, Inc. |
|
1500 Avon Street Extended | |
|
Charlottesville, Virginia 22902 | |
ISPYC8-97 Revised: 8/11/97
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||