Sjogren`s Disease
(Prepared by Dr Guillermo Contreras)
![]()
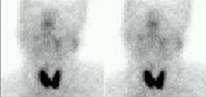
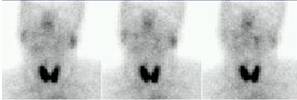
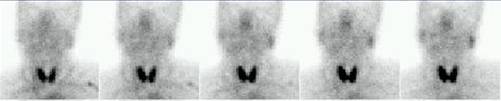
A 49 year old female patient, with the suspicious of Sjogren's Disease. The study
shows mild uptake of parotid glands and the right submandibular gland. The left
submandibular gland did not concentrate the tracer at all. Also, it can be seen
lack of spontaneous salivation into the mouth. Nor after lemon juice stimulus
(Arrow).
Sjogren’s Syndrome is an autoinmune disease characterized by a chronic
inflammatory process involving the salivary and lacrimal glands. The
abnormalities are present in the parotid and at times more intensively in
the submandibular glands.
According to Vinagre et al. an abnormal salivary gland scintigraphy result is accepted by the American-European consensus group as a criterion for the diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome. Scintigraphic evaluation of salivary gland function also plays an important role in therapeutic decision and patient follow-up.
References:
1 Kazuya Shizukuishi. Scoring analysis of salivary gland scitigraphy in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Annals of Nuclear Medicine, vol 17, pages 627-631, 2003.
2
Vinagre F, Santos MJ, Prata A, da Silva JC, Santos AI.Assessment of salivary
gland function in Sjögren's syndrome: the role of salivary gland scintigraphy.
Autoimmun Rev. 2009 Jul;8(8):672-6.