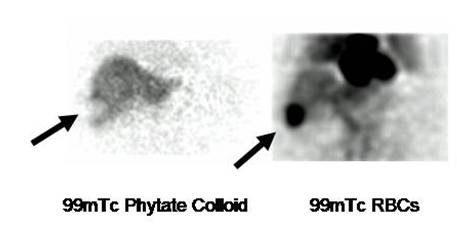
Liver Hemangioma (Prepared by Dr Gabriel Castro, Costa Rica).

Female 37 year old, who presented with a mass on ultrasound. Note the defect in
the right lobe on colloid scan, which shows intense vascularization on the
Spect RBCs exam (arrows).
Tc-99m RBC SPECT scintigraphy is a helpful noninvasive technique in the
diagnosis of hepatic hemangioma, especially in those at risk for lesion rupture
or bleeding. The use of ultrasound should precede scintigraphy for two important
reasons: the size and the location of the lesion. Location of the lesion
(anterior or posterior) is important for optimal gamma camera acquisition
parameters. Lesions less than 1 cm are difficult to detect because they are
beyond the limit of spatial resolution of the gamma camera (1).
Noninvasive diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma of the liver is an important step
in the investigation of patients with focal hepatic lesions since biopsy may
result in life-threatening hemorrhage. The technique shows the characteristic
scintigraphic pattern of blood-pooling on delayed images. Specificity for
hemangiomas greater than 1.9 cm is 100% (2).
References:
1 Desouki M,
Mohamadiyeh M et al. Features of hepatic cavernous hemangioma on planar and
SPECT Tc-99m-labeled red blood cell scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 1999
Aug;24(8):583-9.
2 Farlow D, Chapman P et al. Investigation of focal hepatic lesions: is
tomographic red blood cell imaging useful? . World J Surg. 1990
Jul-Aug;14(4):463-7.