HepatoPulmonary Syndrome
(Prepared by:Dr Raul Collado).
Female, 13 years of age with history of hepatitis at 5 years, initially classified as hepatitis A. Nonetheless, progresses to liver cirrhosis. Also hypertension was detected, whose study showed idiopathic hypercalciuria and right ureteral stones and secondary hydroureteronephrosis. Evolves with portal hypertension syndrome and several episodes of gastrointestinal bleeding from esophageal and gastric varices grade II. Abdominal Doppler: Hypoechoic noduliforme image in segment V of liver, size 23 x 16 mm. Elevated alpha-fetoprotein 1260 ng/ml and at 2 months of age was 1637 ng/ml. Later on, hepatopulmonary syndrome ensues. V/Q scintigraphy : Multiple AV fistulas in the lungs. Magnetic Resonance: Signs of advanced chronic liver damage and portal hypertension. Moderate hepatomegaly. Nodule in hepatic segment V suspicious of HCC. Echocardiography: positive for hepatopulmonary syndrome. V/Q scintigraphy : evidence of significant right to left shunt (38%). Note brain, thyroid, liver, spleen and kidneys with marked radiotracer activity. Bronchopulmonary Evaluation: Parameters of pO2, alveolar gradient and V/Q scintigraphy consistent with a severe hepatopulmonary syndrome. Patient is candidate for liver transplantation .
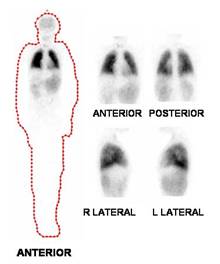
The hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) comprises advanced chronic liver disease
(CLD), arterial hypoxemia and intrapulmonary arteriovenous shunting in the
absence of a primary cardiopulmonary disease. HPS has been more frequently
reported in adults than in children with no data on its prevalence in
children with CLD. The presence of shunts was significantly correlated with the
duration of CLD, clinical findings, presence of cirrhosis and porto-systemic
collaterals. We calculated for each patient a shunt index (SI) by the
formula: (activity outside thorax/activity outside plus inside thorax) 100; and
an SI value of 0.278 was found to be a cutoff value for shunt detection. All
patients with SI above this value had shunting associated with hypoxemia and all
patients with SI below this value had no hypoxemia (specificity 100%). Arterial
hypoxemia and intrapulmonary shunts were diagnosed in 17.5% of this cohort of
children with cirrhotic or noncirrhotic CLD representing the classic HPS.
Tc-MAA perfusion lung scan was more sensitive than CEE in detection of
intrapulmonary shunts.
References:
1 El-Shabrawi MH, Omran S,
Wageeh S, Isa M, Okasha S, Mohsen NA, Zekry O, E-Bartan G, El-Karaksy HM.
(99m)Technetium-macroaggregated albumin perfusion lung scan versus contrast
enhanced echocardiography in the diagnosis of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in
children with chronic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010
Aug;22(8):1006-12.