Acute Tubular Necrosis

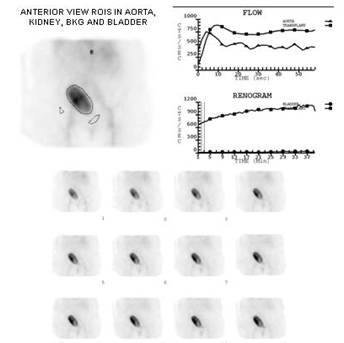
Female 52 year old, bearing chronic renal insuficiency of unknown origin, up until recently on hemodyalisis and who underwent bank kidney transplantation 4 days ago. Time for cold ischemia was 16 h 30 min and for warm ischemia 33 min. As of first day diuresis dropped significantly. Kidney in right inferior abdominal quadrant with normal size and excellent perfusion, synchronous to the aorta (upper, time activity curves). Bottom, images from 1 min to 30 min show good uptake and little excretion into the bladder. The kidney renogram depicts severe retention and that of the bladder is flat and with no increment in regard to baseline.
This pattern is typical for acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and very common in bank organ transplant (40%), as compared to less than 5% of living donor grafts. 99mTc-MAG-3 renogram is adequate for diagnosis and follow up. Sensitivity is around 80% to 90%. Studies with 99mTc MAG-3 have shown that acute rejection can be distinguished from ATN by changes in serial studies. When sequential studies show a progressive decrease in perfusion of the kidney with a primary diagnosis of NTA, then the associated probability of rejection is high.
References:
Etchebere, Elba, Ramos Celso Dario y Camargo, Edwaldo. Trasplante Renal.p: 425-433 en: Medicina Nuclear Aplicaciones Clínicas. Eds: I. Carrio - P. González. Editorial Masson, Barcelona España, 2003.
Home Index Clinical Applications Renal Transplant Evaluation