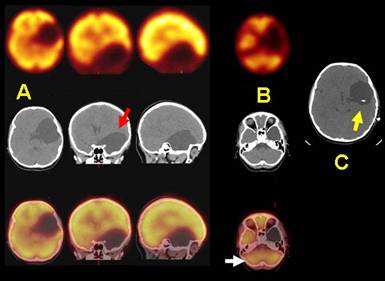
ARACHNOID CYST (Prepared by Dr Gabriel Castro)

6 y/o male with no prior diseases, presented with a seizure episode. A: CT (middle, red arrow) : Arachnoid cyst in left mid temporal lobe. The Tc99m ECD SPECT showed a rounded area of marked hypoperfusion concordant with CT lesion in the fusion image (bottom). B: Note decreased perfusión in the right cerebelar hemisphere compatible with diaschisis, defined as inhibition of function in an area of the brain remote, but anatomically connected through transynaptic neural pathways, to the site of primary injury (white arrow). The rest of the cerebral cortex perfusion is preserved. C: The patient was treated with cyst-peritoneal shunting (see image with yellow arrow)), with improvement.
Arachnoid cysts (ACs) are intra-arachnoid collections of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Primary congenital lesions within the arachnoid membrane that expand by CSF secretion (1). ACs that exert a mass effect, particularly those in children, should be treated. Surgical options include drainage by needle aspiration or burr hole evacuation; craniotomy for cyst excision or marsupialization into the subarachnoid space, basilar cisterns, or ventricles; and cyst-peritoneal shunting (2). The management of asymptomatic individuals, who present with large cysts, is controversial. Cerebral SPECT shows impaired brain perfusion in 70% of symptomatic patients. The zone of decreased rCBF corresponds well with clinical symptoms and with neuroimaging findings. Constitutes a valuable adjunct tool for correlating regional function with brain anatomy, and may be of help to allocate patients with ACs for surgical treatment or clinical observation. (3) .
References:
1) Griffith H et al: Intracranial arachnoid cysts in children. J Neurosurg 64:835-842, 1986.
2)2) Galassi E, Piazza G, Gaist G, et al: Arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa: a clinical and radiological study of 25 cases treated surgically. Surg Neurol 14:211–219, 1980.
3) Martínez J et al. Functional assessment of intracranial arachnoid cysts with TC99 m-HMPAO SPECT: a preliminary report. Childs Nerv Syst (2006) 22: 1091–1097.
Home Index 99mTc-HMPAO Brain SPECT 99mTc-ECD Brain SPECT Clinical Applications