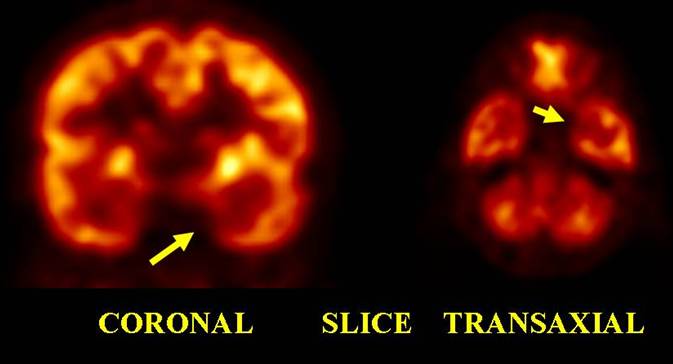

Temporal lobe Epilepsy Refractary to therapy
Thirteen year old male with refractary epilepsy. It was suspected clinically frontal dysplasia. Arrows show a small metabolic defect in the mesial aspect of the left temporal lobe consistent with an epileptogenic focus.
In the paper from Lee KK et al, several interesting comments, quoted below, are discussed, in agreement with the author experience regarding this procedure. The MRI and FDG fusion can be made easily if the anatomic acquisition parameter are known and matched in the FDG acquisition.
Epilepsy is a chronic disorder affecting approximately 1% of the population of the world. Approximately one third of patients with epilepsy remain refractory to medical therapy. For these patients, surgery is a curative option.
MR imaging still fails to reveal any apparent abnormality in approximately 20% of the patients with medically refractory epilepsy.
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) is the most frequent form of partial epilepsy. It is estimated that 60%–75% of patients with MTLE have MESIAL TEMPORAL SCLEROSIS, which is characterized by neuronal loss and gliosis of mesial temporal structures, including the hippocampus, amygdala, and parahippocampal gyrus. The epilepsy associated with MTS is most often medically refractory, but surgical intervention is relatively effective with 48%–84% of patients being seizure-free after surgery.
FDG-PET detects hypometabolism in approximatley 80% of patients with unilateral MTLE.
FDG-PET can sometimes falsely localize the epileptogenic activity. Hypometabolism is the typical finding on interictal FDG-PET. However, in ictal studies, FDG-PET may show hypermetabolism. Furthermore, ictal FDG-PET is often difficult to interpret because it often reveals complex patterns of both hypometabolism and hypermetabolism.
References:
1 Quirce R. and Carril J.M. Spect y PET en la enfermedad cerebrovascular, p: 437-447; Mut F Demencias 453-464; Jimenez VA et al Tomografia por Emision de Positrones en el Diagnostico de los tumores del sistema nervioso central, p481-489 in: Medicina Nuclear Aplicaciones Clínicas. Eds: I. Carrio - P. González. Editorial Masson, Barcelona España, 2003.
2 Lee KK, Salamon N.[18F] fluorodeoxyglucose-positron-emission
tomography and MR imaging coregistration for presurgical evaluation of medically
refractory epilepsy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Nov;30(10):1811-6. Epub 2009 Jul
23.
Home Index Neuropsychiatric Procedures 18F-FDG Brain Imaging Clinical Applications