CHOLINE NORMAL IMAGES
Prepared with the collaboration of Dr. Eduardo Swett

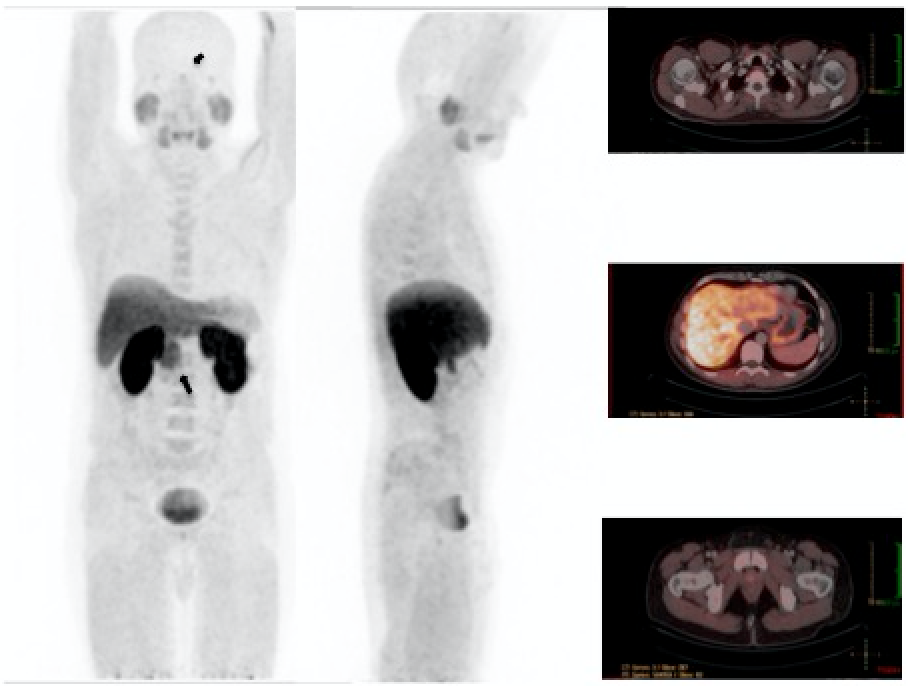
Male, 37 year old, with primary hyperparathyroidism. Asymptomatic, Hybrid image SPECT/CT with 99mTc-Sestamibi was negative for hyperfunctionant parathyroid tissue. It was requested a 18F-Choline PET-CT looking for the cause of hyperparathyroidism.
The images showed moderate physiological activity in pituitary gland (small arrow), salivary glands, intense in the liver, mild in spleen, bone marrow, pancreas at the uncinate process (large arrow) and kidneys. Urinary excretion of 18 F-choline can cause difficulties in evaluating pathological uptake in prostate bed. Patients should be well hydrated and void before acquisition.
Choline is a substrate for the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine, which is a major phospholipid compound in the cell membrane. Increased choline uptake reflects proliferative activity by estimating membrane lipid synthesis.
References:
1 Ackerstaff E, Glunde K, Bhujwalla ZM. Choline phospholipid metabolism: a target in cancer cells? J Cell Biochem. 2003;90: 525–33.
2 Kitajima K, Murphy RC, Nathan MA. Choline PET/CT for imaging prostate cancer: an update. Ann Nucl Med. 2013 Aug;27(7):581-91.
3 Michaud L, Burgess A, Huchet V, Lefèvre M, Tassart M, Ohnona J, Kerrou K, Balogova S, Talbot JN, Périé S. Is 18F-fluorocholine-positron emission tomography/computerized tomography a new imaging tool for detecting hyperfunctioning parathyroid glands in primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism?. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Dec;99(12):4531-6.
4 Mertens K, Ham H, Deblaere K, Kalala JP, Van den Broecke C, Slaets D, De Vos F, Goethals I. Distribution patterns of 18F-labelled fluoromethylcholine in normal structures and tumors of the head: a PET/MRI evaluation.Clin Nucl Med. 2012 Aug;37(8):e196-203. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e31824c5dd0.